|
No pierda la oportunidad de ver las ventajas del COMPROBADOR INTELIGENTE DE BATERÍAS GOLD-IBT.
What is a battery?
A battery is an electric storage device which can be found in any number of shapes, sizes, voltages and capacities.
This manual is concerned only with one battery technology - the most successful - lead acid - lead and lead oxide immersed in sulphuric acid. Each cell having a 2 volt potential. A battery is simply a number of cells connected together with a given voltage and capacity. The more cells the higher the voltage, the larger the plates the higher the capacity (in general).
There are two concepts in lead-acid batteries
There are three basic applications
WARNING - DO NOT USE THE WRONG BATTERY FOR THE APPLICATION. This guide is focused on Industrial Standby applications and NOT Automotive and Traction use.
Industrial batteries are available from two distinct groups with the following features. Note that VRLA have superseded open-vented in many applications.
Note - the term sealed lead-acid SLA is an old acronym considered misleading and is now replaced by Valve Regulated Lead Acid VRLA.
The Yuasa range focuses on VRLA technology.
To optimise battery duty and life for your application, make sure you choose the right product from the Yuasa range.
As mentioned earlier, batteries come in all shapes and sizes, from types no larger than a shirt button, to a battery system filling an entire room. To find the size of battery you require you generally need two pieces of information battery load and back-up times. (Note; other factors may also have an effect).
Battery Load Whether you power lights, motors, electronic equipment or a toy vehicle your equipment will draw a load in AMPS. If this is unknown then the equipment will have a rating expressed in Watts which may simply be converted to Amps by dividing the value by the normal voltage of the system. Example You have chosen NPC for high cycle life and wish to drive a power tool rated at 120 watts 12 volts. Load current = 120 divided by 12 = 10 Amps
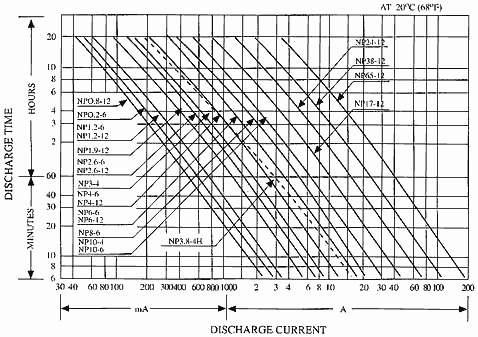
Back-up time This is the time you require the battery to support the load described above and is often called Autonomy or discharge time. Example, To power a cordless electric tool for a total of 3.0 hours before recharging. With these two pieces of information use our selection graph to plot an intersection point from which you will determine a required size or capacity in Amp. hours (Ah). Our figure No. 1 has been rationalised into rounded figures of capacity. If your intersection point falls between two lines choose the next highest value. Fig No.1 NP Types
Always choose a suitable sized battery from the ranges appropriate to your application. You may notice that the chosen capacity in Amp hours is often higher than the Value of Amps x Hours used, in our example using 10 AMPS x 3 HRS = 30 Ah and the chosen option being 38Ah. This is because the capacity 'cA' of each NP battery is stated at the 20 hour discharge rate. You will only get full capacity if discharged over this length of time. Note:- This explanation is a simplified version, if in any doubt call our Technical department on 01793-645753.
Correct charging of a VRLA battery is essential in optimising battery performance and life. Although a constant voltage charge should be applied, optimum charging also depends on temperature (Nominally 20°C), charge current (max 1/4 battery capacity) and ripple current (minimum). Two basic categories of charging exist. Float/Standby This charging method is used in applications such as emergency back-up when the battery is required only upon mains failure e.g., Alarm Panels, Emergency Lighting, UPS. In each case the battery is continuously on charge and consequently the recommended voltages are slightly lower than cyclic charging so as not to damage the battery. (Float voltage for Yuasa NP range = 2.25-2.3 volts/cell). These figures may vary between different battery types. Cyclic Cyclic charging is used in applications where the battery is repeatedly discharged then charged, e.g. Portable equipment, Wheel Chairs, Golf trolleys etc. A higher charging voltage is used but should NEVER be left on indefinitely since it will overcharge and destroy the battery. (Cyclic voltage for Yuasa NP range = 2.4 - 2.5 volts/cell) For optimum performance always recharge a battery immediately after discharging. Note - Consult the individual battery specification for the correct charging voltage or contact Yuasa Technical Department on 01793-645753
The storage or shelf life of a VRLA battery is usually between 12 to 18 months at 20°C starting from a charged condition. Warning - Never store in a discharged or partially discharged state. Always store in a dry, clean, cool environment in a fully packaged condition. If storage of 12 months or longer is required supplementary charging will be required.
Design Life Float Cyclic Near the end-of-life the standby capacity of the battery will reduce. When this reduction becomes persistently regular, this indication can also be used for the time of replacement.
Each Yuasa VRLA battery should be supplied in a charged condition having passed stringent quality checks. To ensure optimum battery performance and life, it helps to take care of your battery by observing the following:
WARNING - Never leave a VRLA Battery in a discharged state. If a battery has an open-circuit voltage lower than its rated value, then sulphation may well be the cause. When a battery is left in a discharged state or for prolonged periods of storage lead sulphate crystals begin to form acting as a barrier to recharge and will prevent normal battery operation. Depending on the degree of sulphation, a battery may be recovered from this condition by constant current charging at a higher voltage with the current limited to one tenth of the battery capacity for a maximum of 12 hours. Note the applied voltage will exceed the normal recommendation and so the battery must be monitored (not left unattend) and removed from charge if excess heat is dissipated. The voltage required to "force" this maximum current into the battery will reduce as the battery recovers until normal charging can take place. In extreme circumstances a battery may never fully recover from sulphation and must therefore be replaced. If in doubt call Yuasa Technical Dept 01793-645753
As mentioned in Section 'Charging' optimum charging relies mainly on voltage, current and temperature factors which are interrelated and all of which can cause overcharge. Excessive charge voltages will force a high overcharge current into the battery, which will dissipate as heat, and may cause gas emission through the safety valve. Within a short period of time this will corrode the positive plate material and accelerate the battery towards end-of-life. Under these conditions the heat produced inside the battery can lead to thermal runaway due to the increased electrochemical reaction of the battery. The battery may swell before failing and will be irrecoverable from this state.
Warning -Heat Kills Batteries
The recommended normal operating temperature is 20°° -25°C. HIGH TEMPERATURE will reduce battery service life often quite dramatically (see figures 2 and 3), and in extreme cases can cause Thermal Runaway, resulting in high oxygen/hydrogen gas production and battery swelling. Batteries are irrecoverable from this condition and should be replaced. Figure 2
Notice that high temperatures will give increased performance but only at a loss in life. LOW TEMPERATURES will help to ensure a long service life but batteries used at low temperatures have reduced performance. For detailed information contact Yuasa Technical Dept 01793 - 645753
Do not throw batteries in a bin at end-of-life. VRLA batteries contain substances harmful to the environment so return to your supplier or take to your Council tip for disposal. Caution Never bury in the ground or incinerate at end-of-life. Batteries contain harmful substances making this unsafe.
Return the spent battery to your Stockists, the Local Council tip or any licensed battery dealer for recycling.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
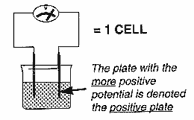 When two materials (often dissimilar
metals) are immersed in a solution they conduct electricity, between
the "plates" causing an electrical potential. The value of this
potential (or voltage) is
dependent
on the materials used,
giving rise to
a whole family of battery types each having benefits
and restrictions in use. Examples are:- lead acid, nickel cadmium (Nicad),
lithium, silver alkaline.
When two materials (often dissimilar
metals) are immersed in a solution they conduct electricity, between
the "plates" causing an electrical potential. The value of this
potential (or voltage) is
dependent
on the materials used,
giving rise to
a whole family of battery types each having benefits
and restrictions in use. Examples are:- lead acid, nickel cadmium (Nicad),
lithium, silver alkaline.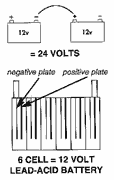


 Finally, when a battery has reached the end-of-life
it must be returned to the point of sale or to a licensed battery dealer
for recycling. Please observe the following points.
Finally, when a battery has reached the end-of-life
it must be returned to the point of sale or to a licensed battery dealer
for recycling. Please observe the following points. Caution
Caution Always
Always